Out of all the pieces of a Web server, the most important part is the hardware involved. Without the server, there would be no use for all the other items talked about, and there would be no Internet.
Server computers are similar to those used by normal users, but are usually much faster, more powerful, and have more memory than regular PCs and laptops. They cost anywhere from $3,000 to over $200,000, and often come with many different elements not found on personal computers. Technological advances have allowed for the size of server hardware to drastically be decreased, which allows for more server computers to be housed in the same space, without expanding the area.

The process of evaluating the performance of Web server hardware and software is called benchmarking, and usually covers the following elements:
- hardware
- operating system software
- server software
- connection speeds
- user capacity
- type of Web pages beig hosted.
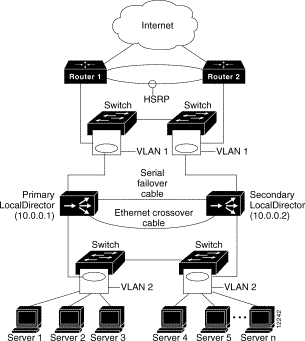
There are two factors used to determine the number of users that will be able to access the site: throughput and response time. Throughput is the number of requests a server can process in a given unit of time, while response time is the amount of time it takes for the server to fulfill one request. Another aspect of server performance involves the server architecture, or the layout of the hardware used in the server.
There are two commonly used server architectures used: server farms or centralized architectures, and distributed or decentralized architectures. Each has both its good and bad points, so it really matters on what options a particular company has.
Some of the good aspects of the centralized architecture include the fact that the server can be monitored in one place, which is an advantage for companies that are limited on space. However, if there is a problem with the server, the whole Web site can go down. This is one of the plus sides to a decentralized architecture since if one section of the server goes down, the rest of the server can keep the Web site up by working a bit more. The one down sided to this type of architecture is that it does require more space to set up, and the initial cost may seem more expensive, even if it does pay for itself over time.
Most decentralized architectures use a load-balancing system that basically allows for the server to manage the flow of users on the server by directing them to the least-congested portion of the server. In a large system, the servers may be organized to handle particular processes.